Table of contents
This tutorial will guide you through the setup on your local machine for editing just the docs sites for our MDLutoronto project.
Prerequisite
Accounts
- GitHub account and to be added to the learning object repository under MDLutoronto GitHub Organization
- See the Manage Student Access to MDLutoronto GitHub Repository guide for instructions on how to add students to the repository.
Software
- Ruby (install the latest x64 version, e.g. Ruby+Devkit 3.4.6-1 (x64))
- Git (install the Windows version)
- VS Code
- Recommended VS Code extensions to install:
- GitLens: for visually using git within VS Code
- Path Autocomplete: for auto-completing file paths when editing markdown files
- Code Spell Checker: for spell checking when editing markdown files
- Recommended VS Code extensions to install:
Configuration
Installing software
A recommended order of installation would be:
- VS Code
- Git
- Ruby
Vs code
For VS Code, you can just keep the default installation options.
Once installed, you may install the recommended extensions listed above via the Extensions view in VS Code (Ctrl+Shift+X), by searching for the extension name and clicking on the Install button.
Or you may install them by visiting the extension links above and clicking on the Install button there. The button will redirect you to VS Code and prompt you to install the extension.
Git
For Git, during the installation, make sure to select the following options when prompted:
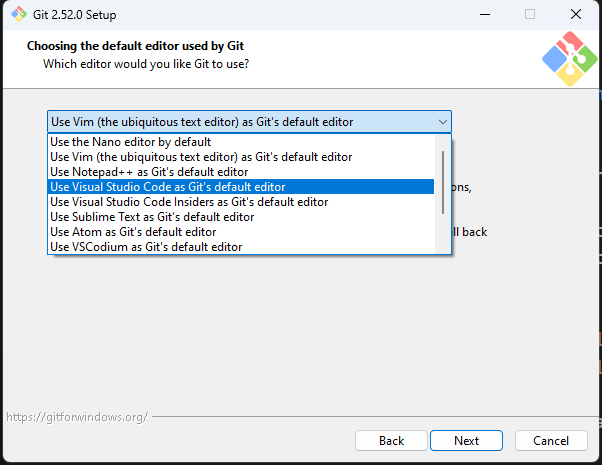
When prompted to select the default editor used by Git, select Use Visual Studio Code as Git’s default editor
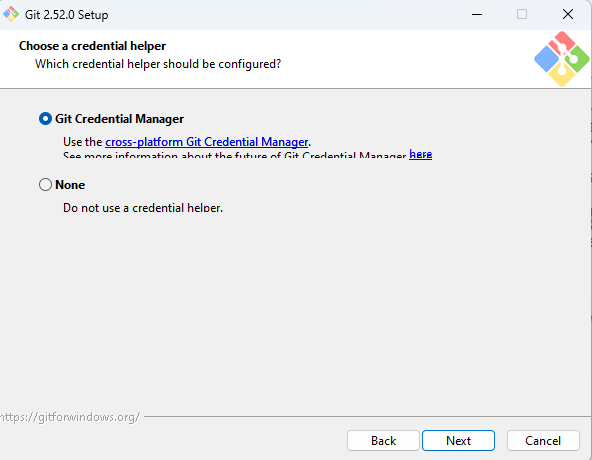
Make sure the Git Credential Manager option is selected to enable Git credential manager for managing GitHub credentials
Once you have installed Git, follow the steps below for configuring Git credential manager and setting up git user.name and user.email.
Connect to GitHub using Git credential manager
Type the following command to make the Git credential manager to manage your GitHub credentials
git config --global credential.helper manageType the following command to login to your GitHub account
git credential-manager github login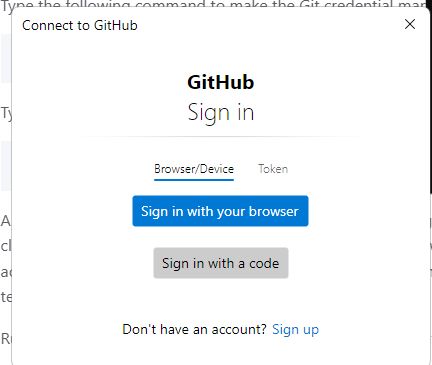
A window (outside the terminal) will pop up and prompt you to login to your GitHub account. Click on the
Sign in with your browserbutton. After logging in, you may close the web browser window and return to the PowerShell terminal.Run the following command to verify your GitHub authentication
git credential-manager github listYou should see your GitHub username printed in the terminal output
Setting up git user.name and user.email
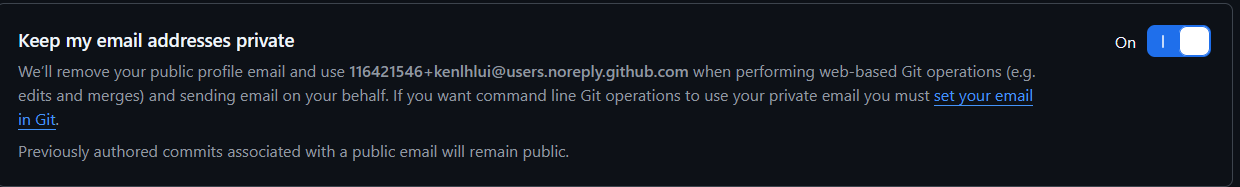
Note that the
user.nameanduser.emailinput will be visible publicly. If you have any concerns, consider using the email relay address for commit provided by GitHub.You can retrieve that email address the under Settings > Emails, after turning on the
Keep my email addresses privateoption
Input the following to set your git user name and email. The email should be the same as the one on your GitHub account (or the email relay address provided by GitHub)
User name can be any name you want to show up on your commits:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"User email should be the email address associated with your GitHub account (or the email relay address provided by GitHub):
git config --global user.email "Your Email"Check your settings with the following command. Look at the
user.emailanduser.namerows. It should show the values you have set above.git config --list
Ruby
For Ruby, during the installation, default options should be fine.
However, at the end of the installation, make sure to check uncheck the Run 'ridk install' to set up MSYS2 and development toolchain option before clicking on the Finish button. 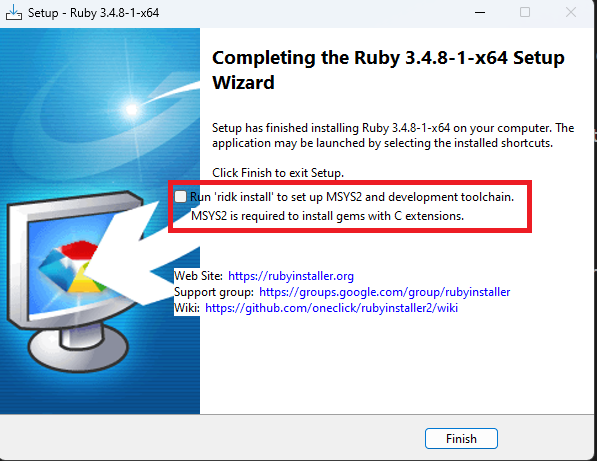
Working with an existing guide
If you are editing an existing guide, you would need to clone (download) the GitHub repository to your local machine first.
Clone the GitHub repository
Here is a sandbox repository to test your access rights/connection: MDLutoronto/just-the-docs-sandbox-stduents After logging in with your account that has access to the MDL GitHub repository, you should be able to view the (private) repository in your web browser.
Get the GitHub repository link to clone
- Go to the intended GitHub repository page in your web browser (e.g. MDLutoronto/jtd-student-sandbox)
- Click on the green
Codebutton on the top right of the repository file list - Make sure the
HTTPStab is selected, then click on the clipboard icon to copy the repository link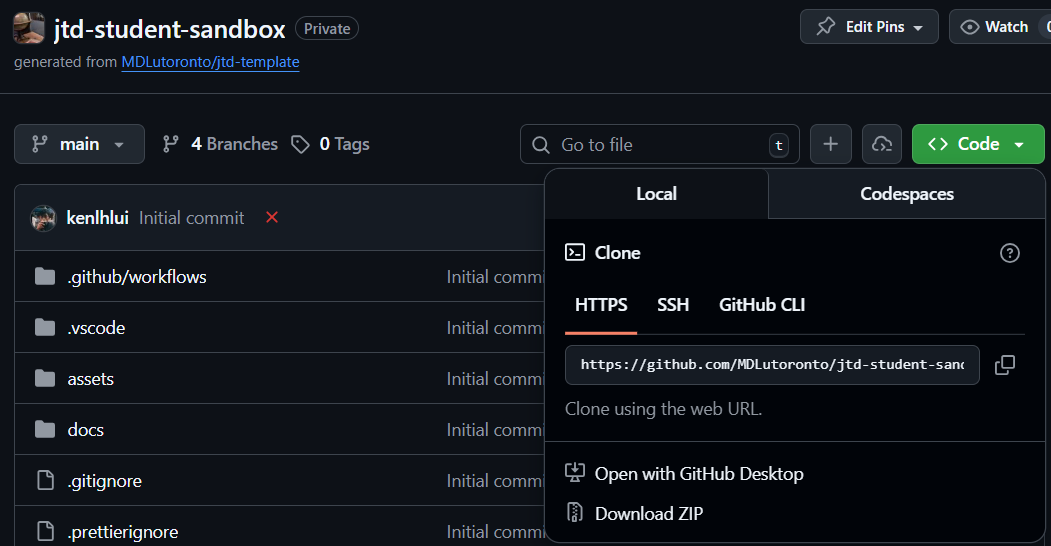
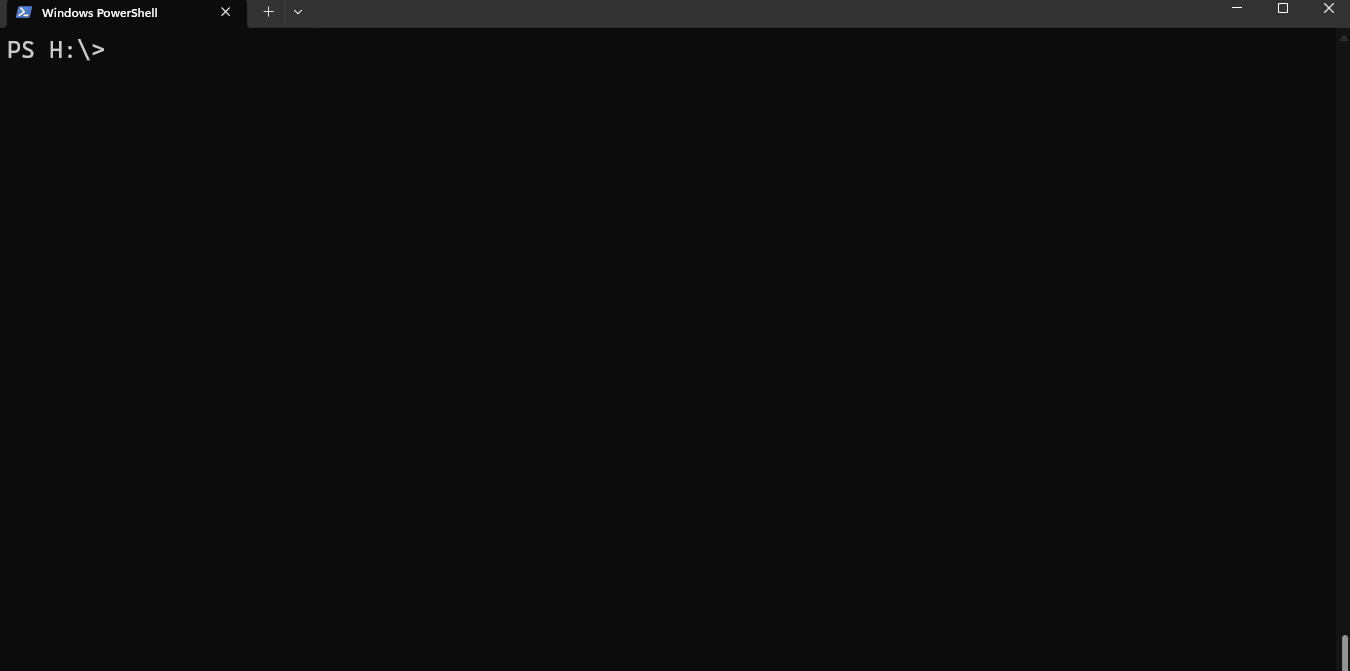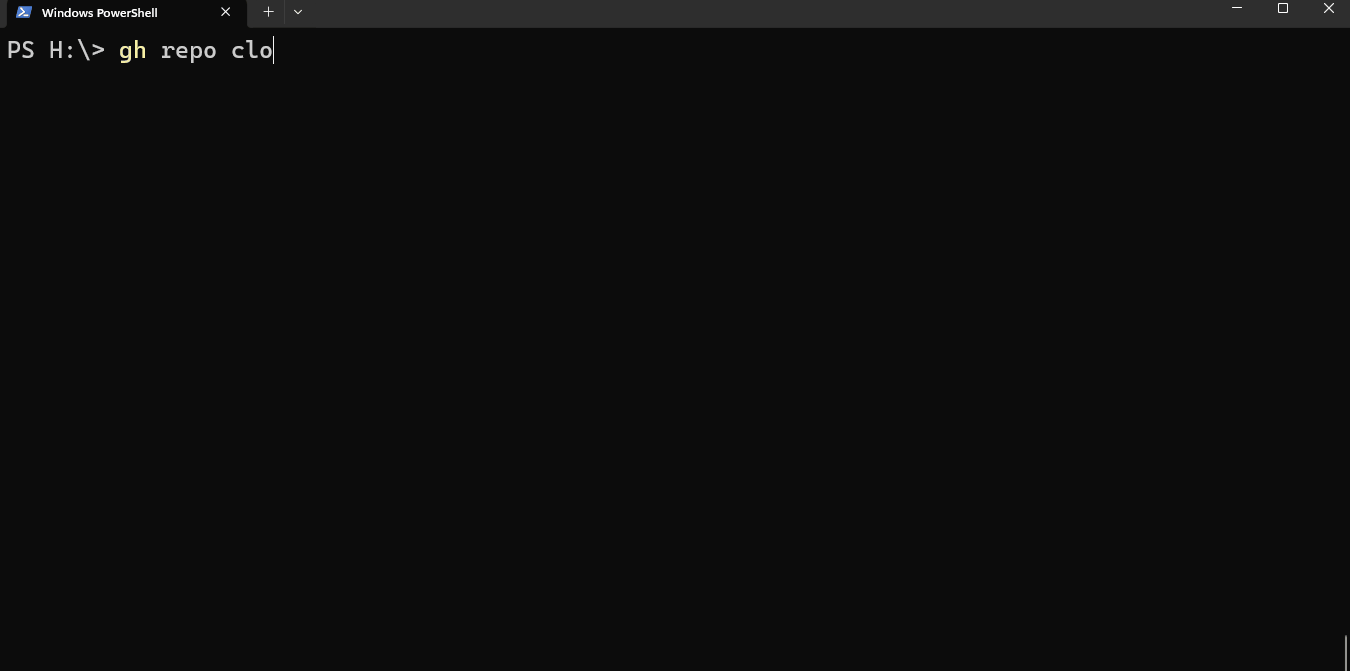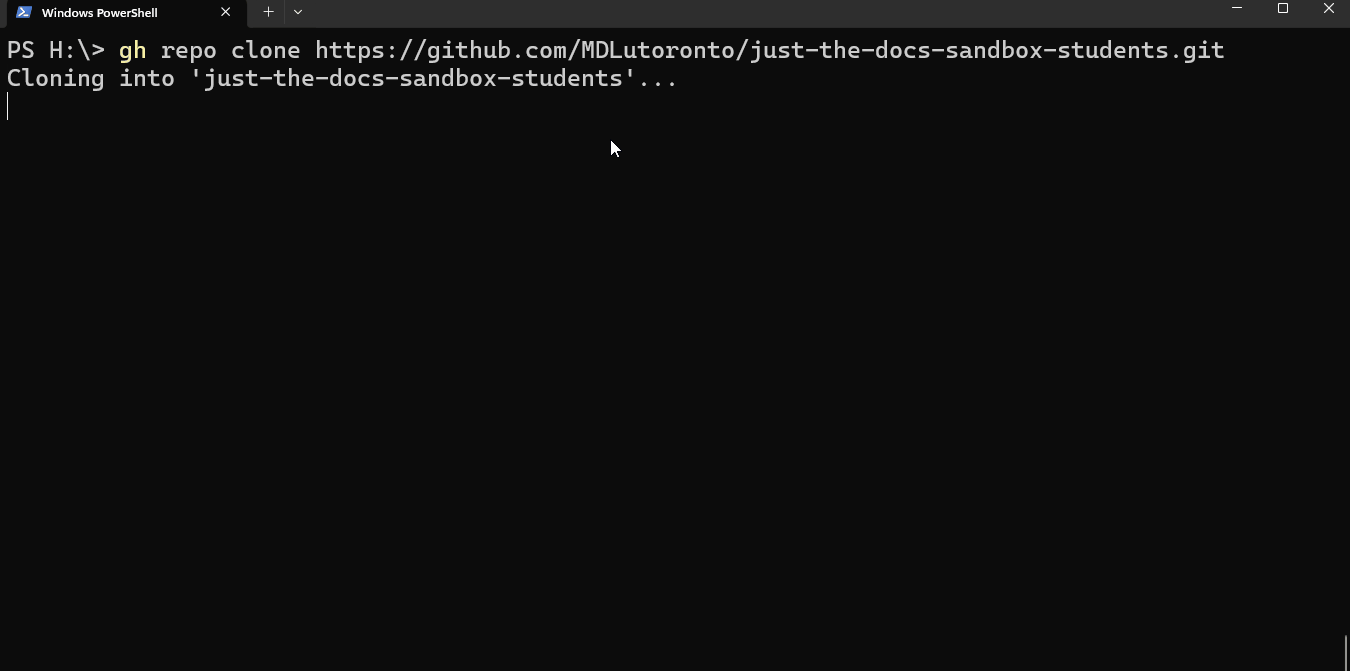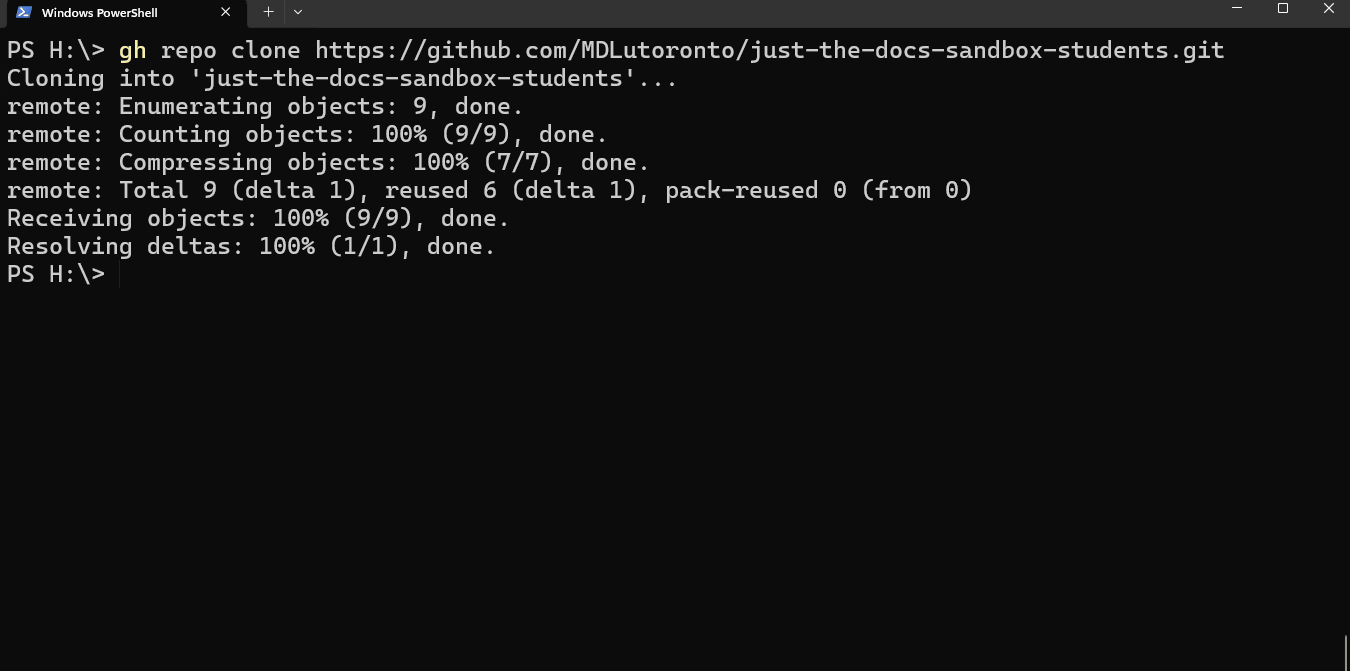
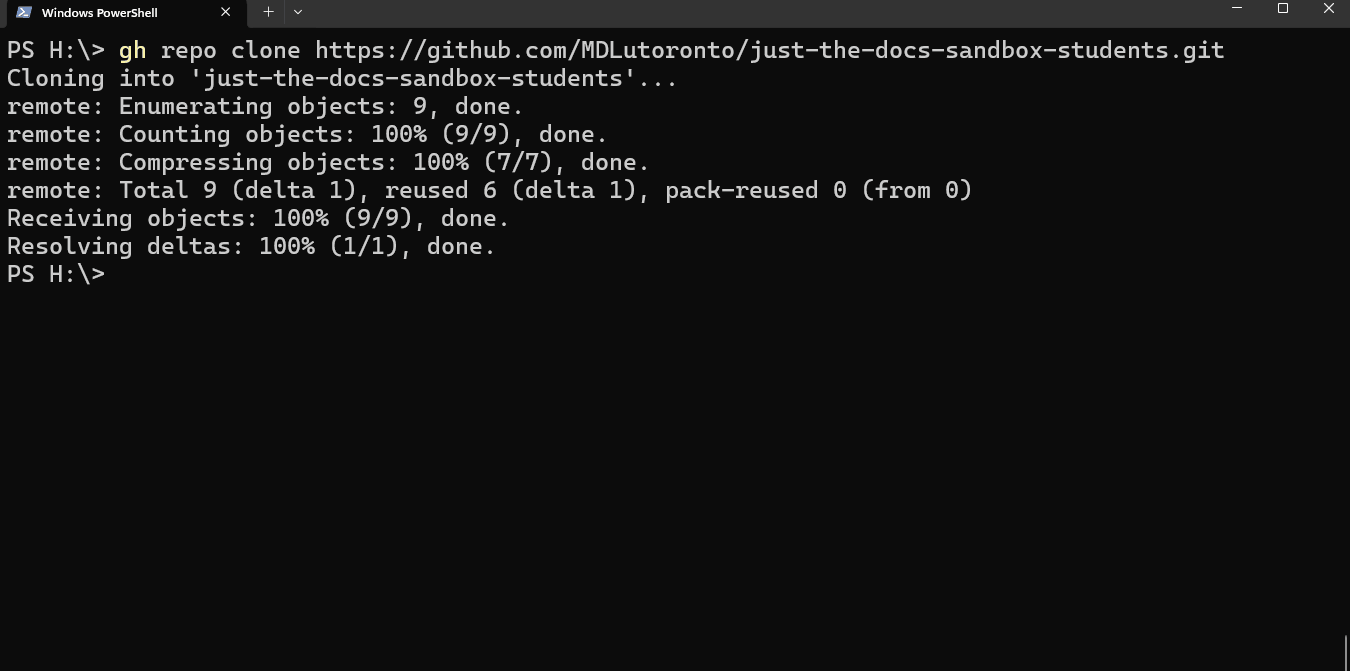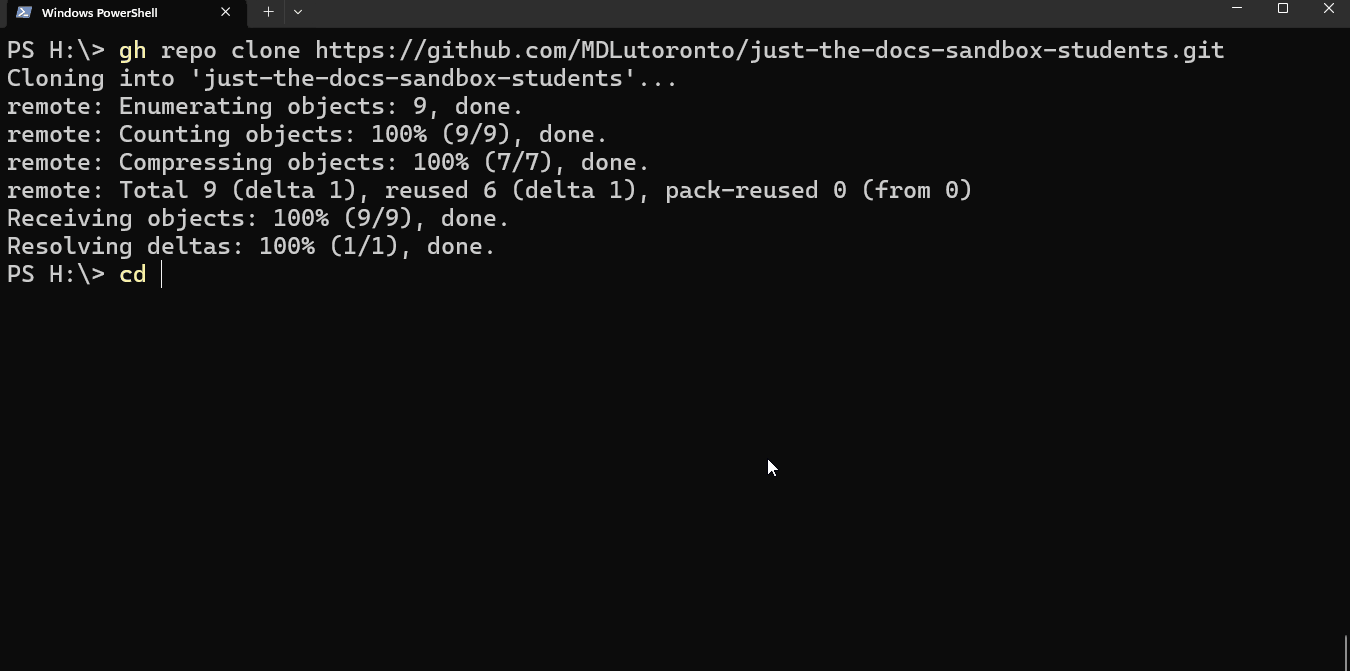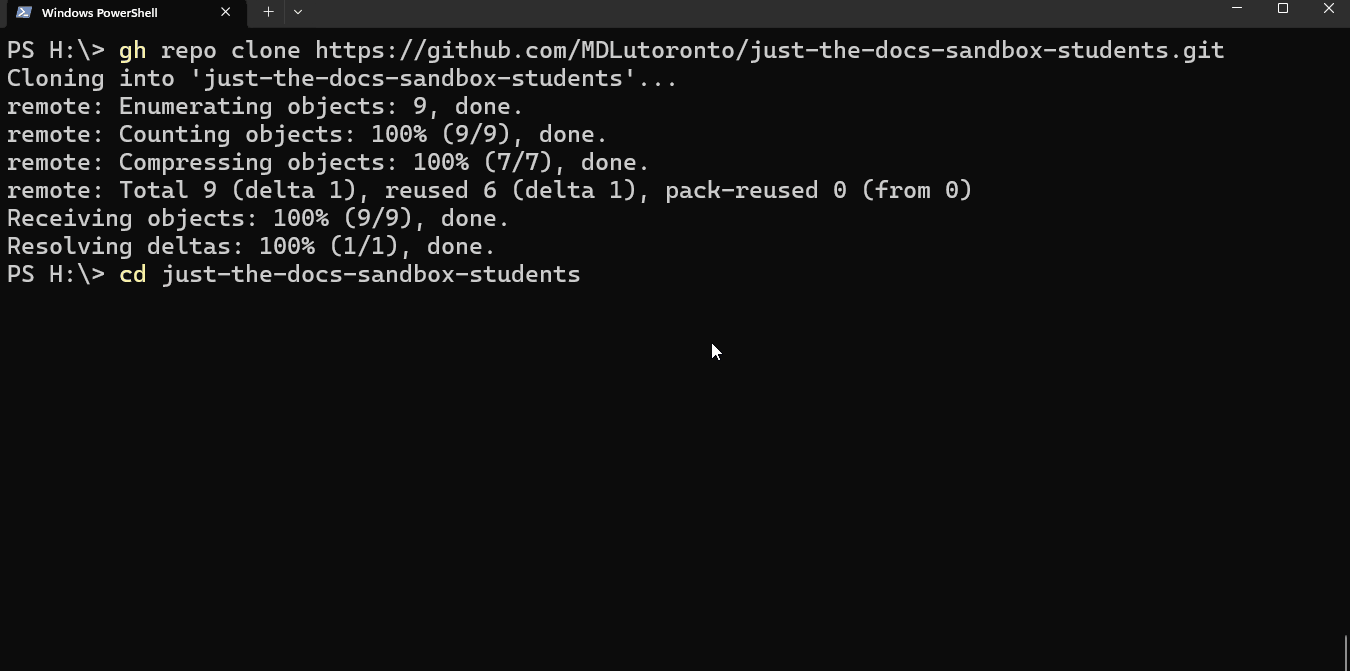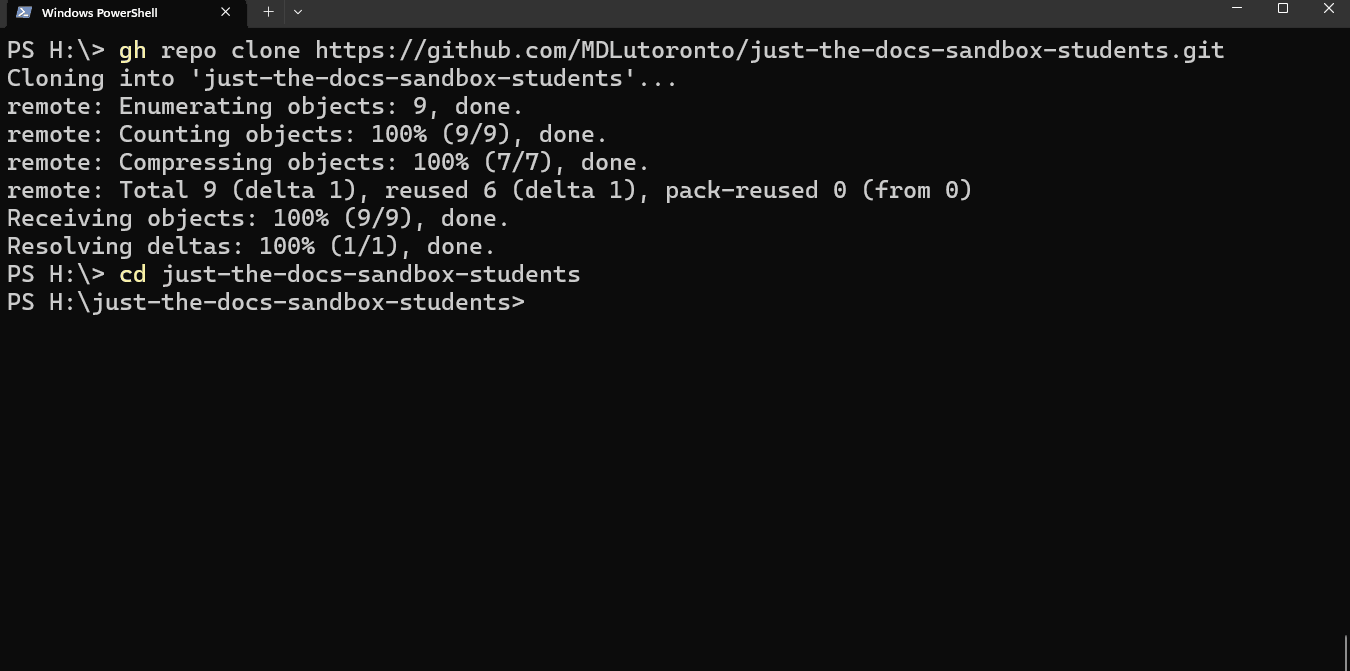
Type the command below in a powershell terminal to clone a GitHub repository. Replace the git_link with the intended GitHub repository link.
git clone $git_linkFor example, if you want to clone the sandbox repository above (with the .git link https://github.com/MDLutoronto/jtd-student-sandbox.git), you will input
git clone https://github.com/MDLutoronto/jtd-student-sandbox.gitTip
You can right-click on the terminal to paste the copied text to the terminal
Enter the repository directory
Once you have cloned the repository, type
cd $directory_nameto change the directory (cd) of the terminal to the repository directory.The
directory_nameby default is the repository name (slug). As for the example above, it isjtd-student-sandboxTip
To utilize the auto-complete function (avoid typing the long string), type a few characters and press
Tabto let the terminal finish it.You should see the prompt in the terminal changed to PS H:\just-the-docs-sandbox-students> with the above example
Type
code .in the terminal to initialize the VS Code for this repository directory.
To preview the website
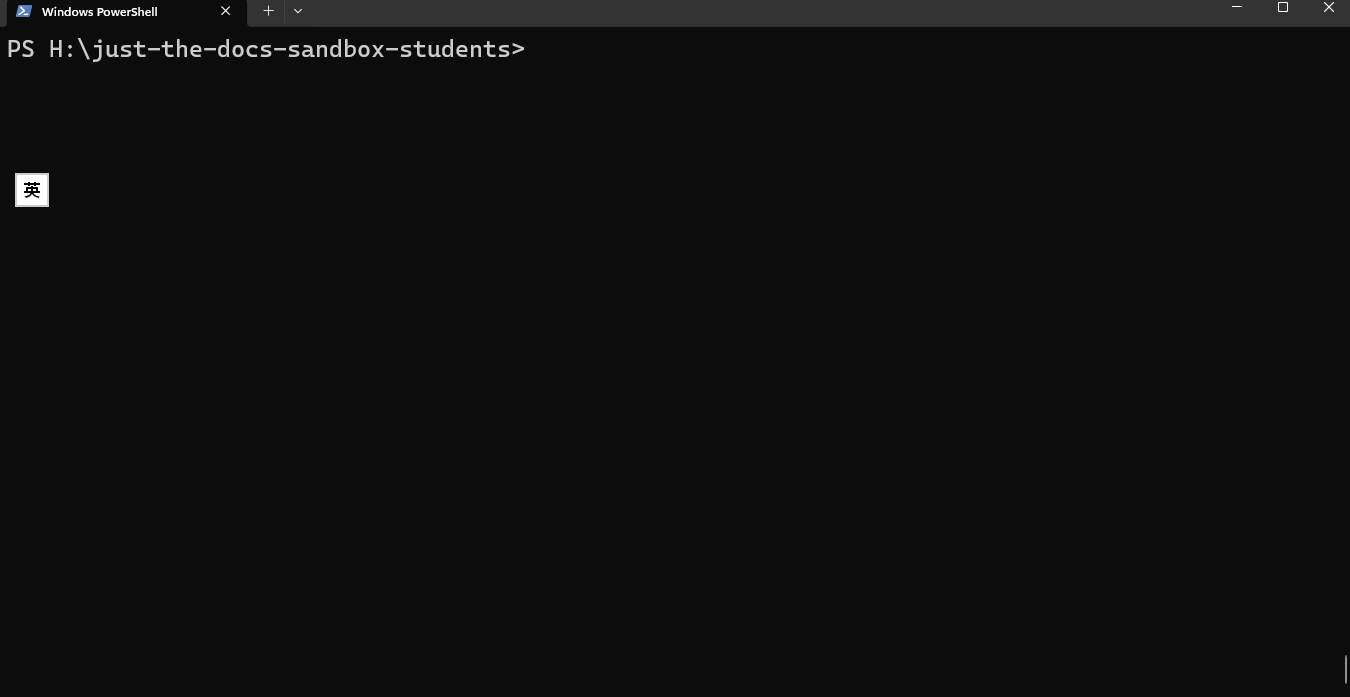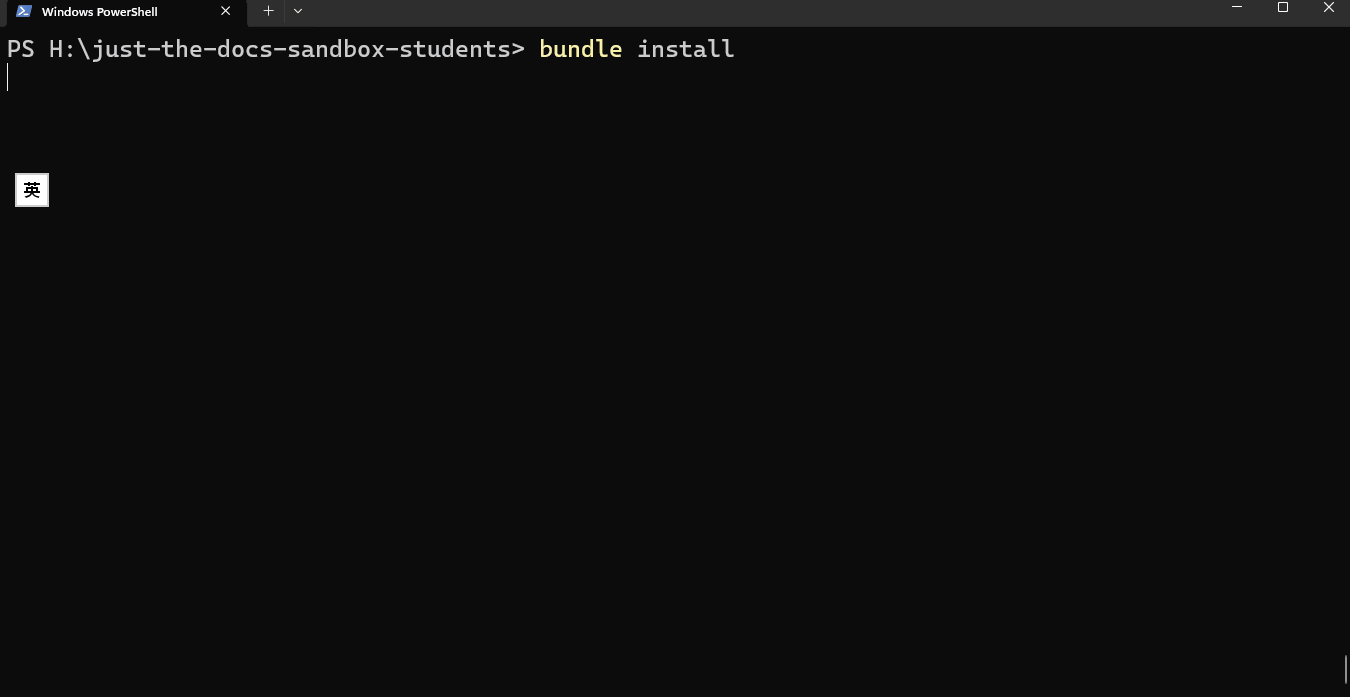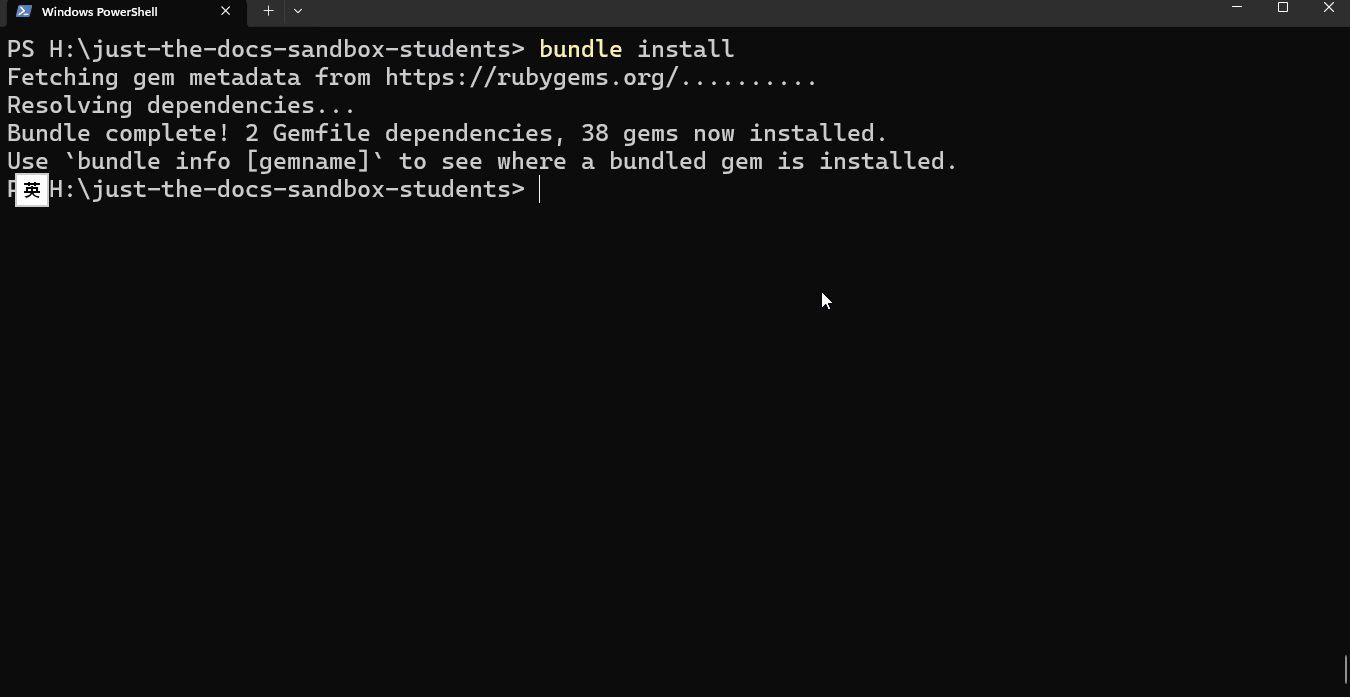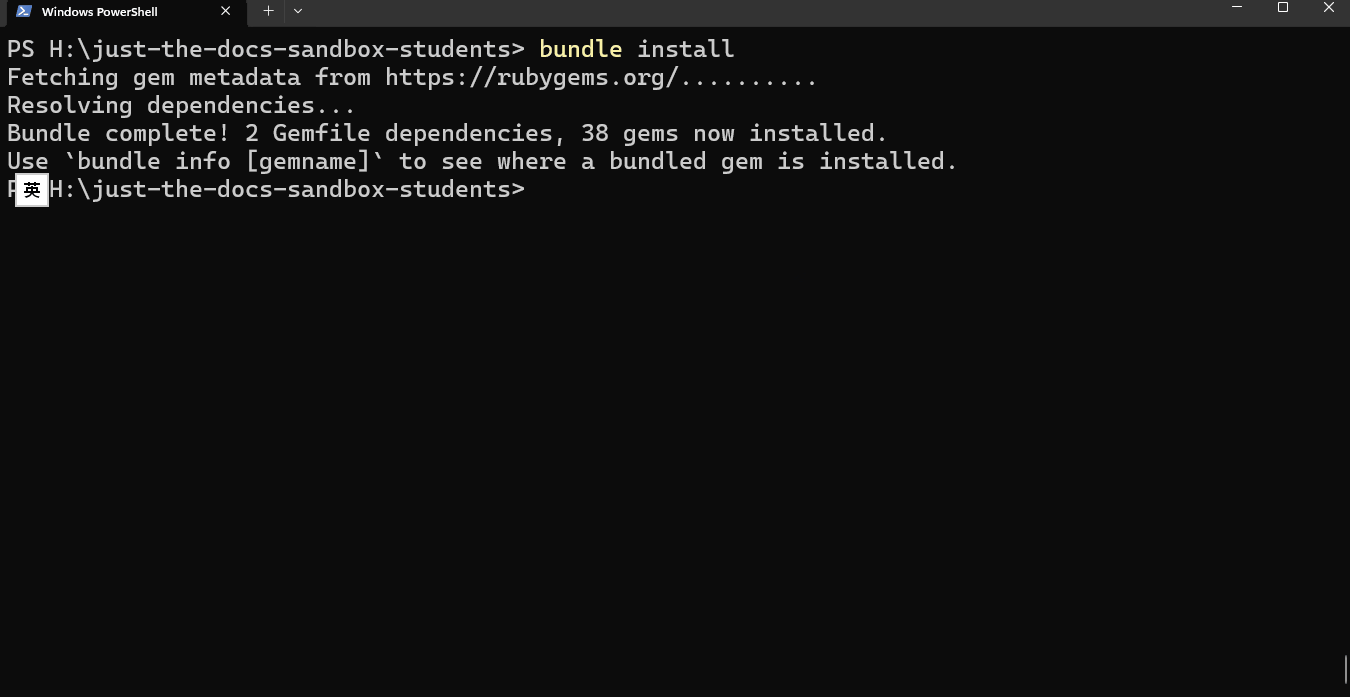
Run bundle install to install the necessary files to start the preview server
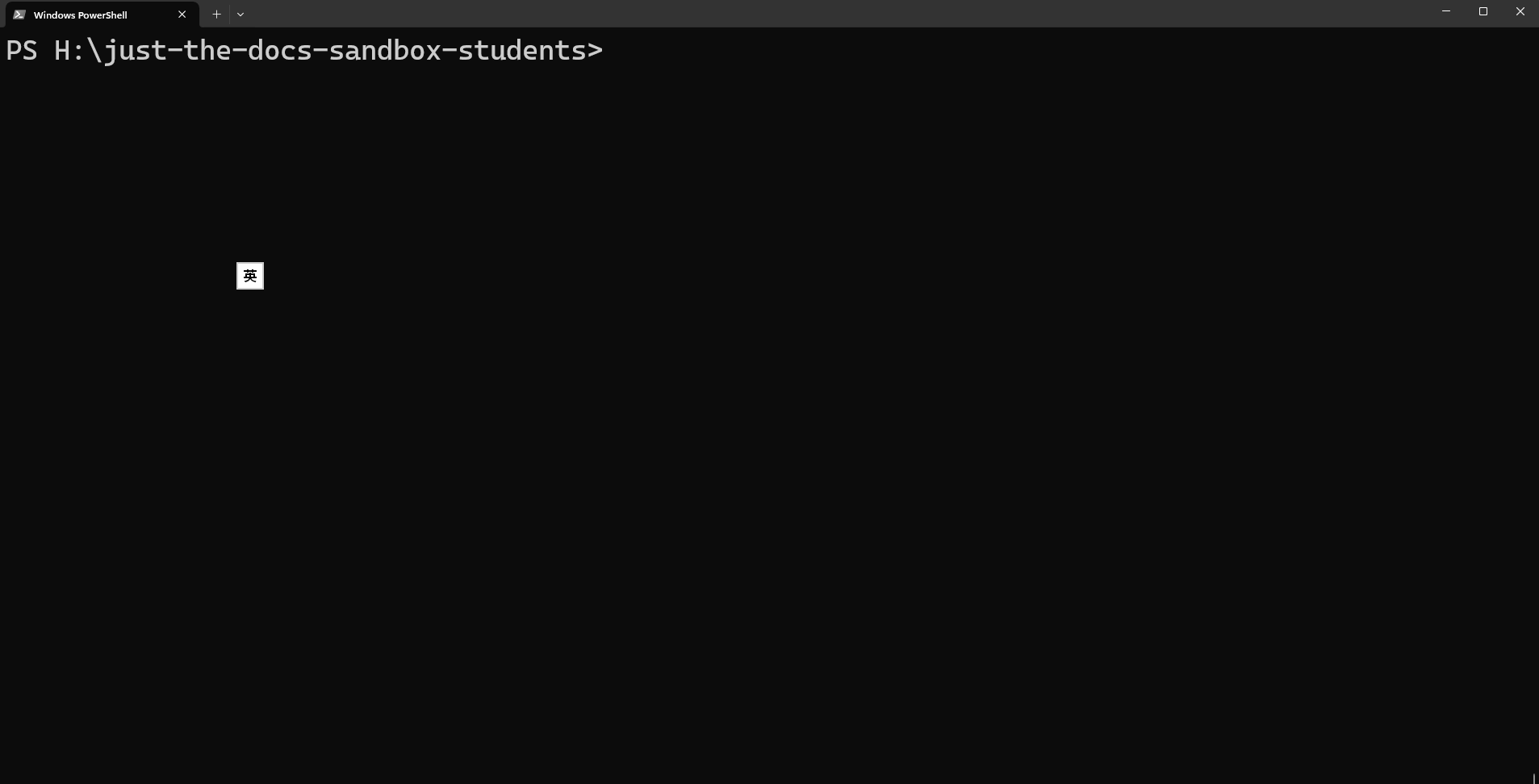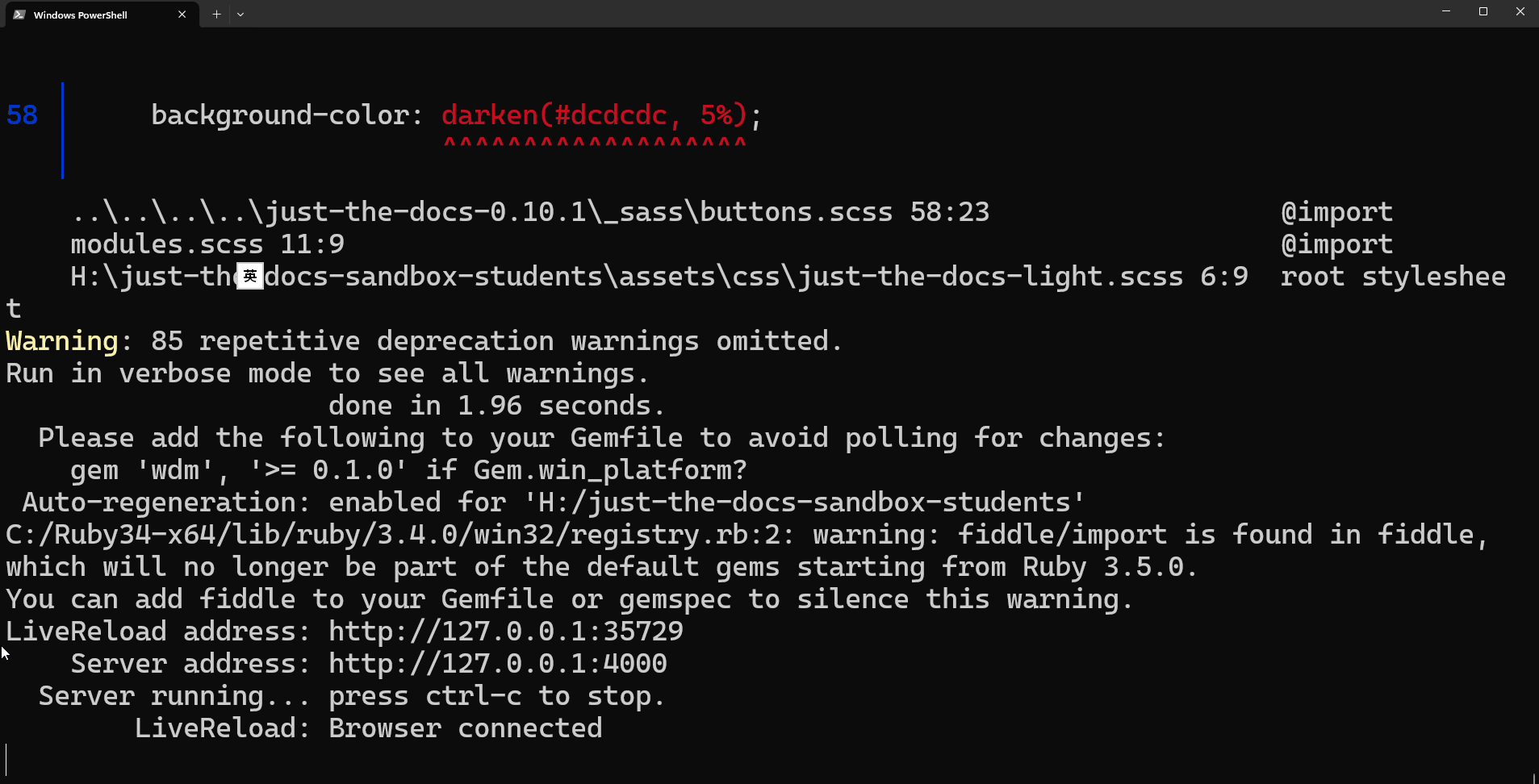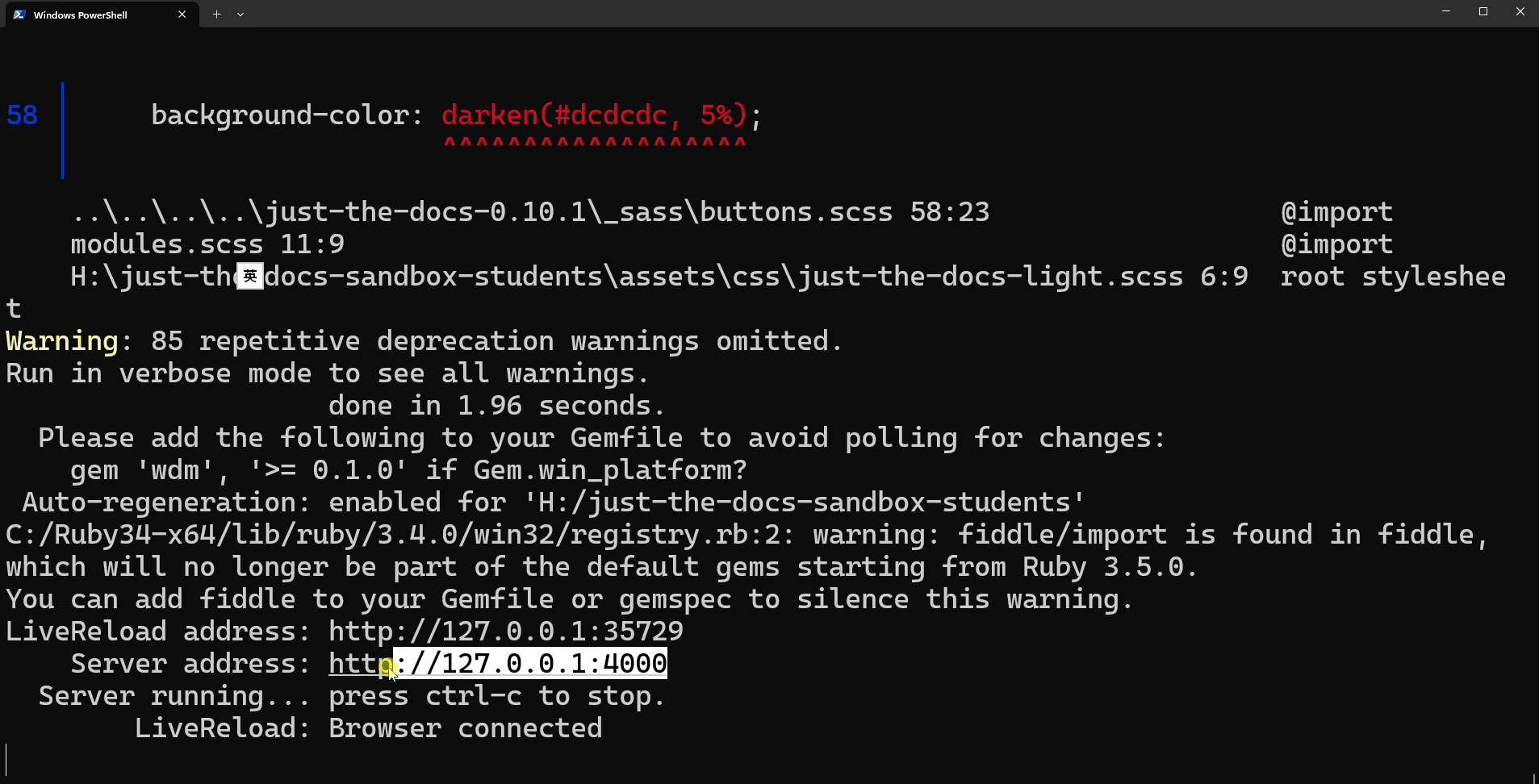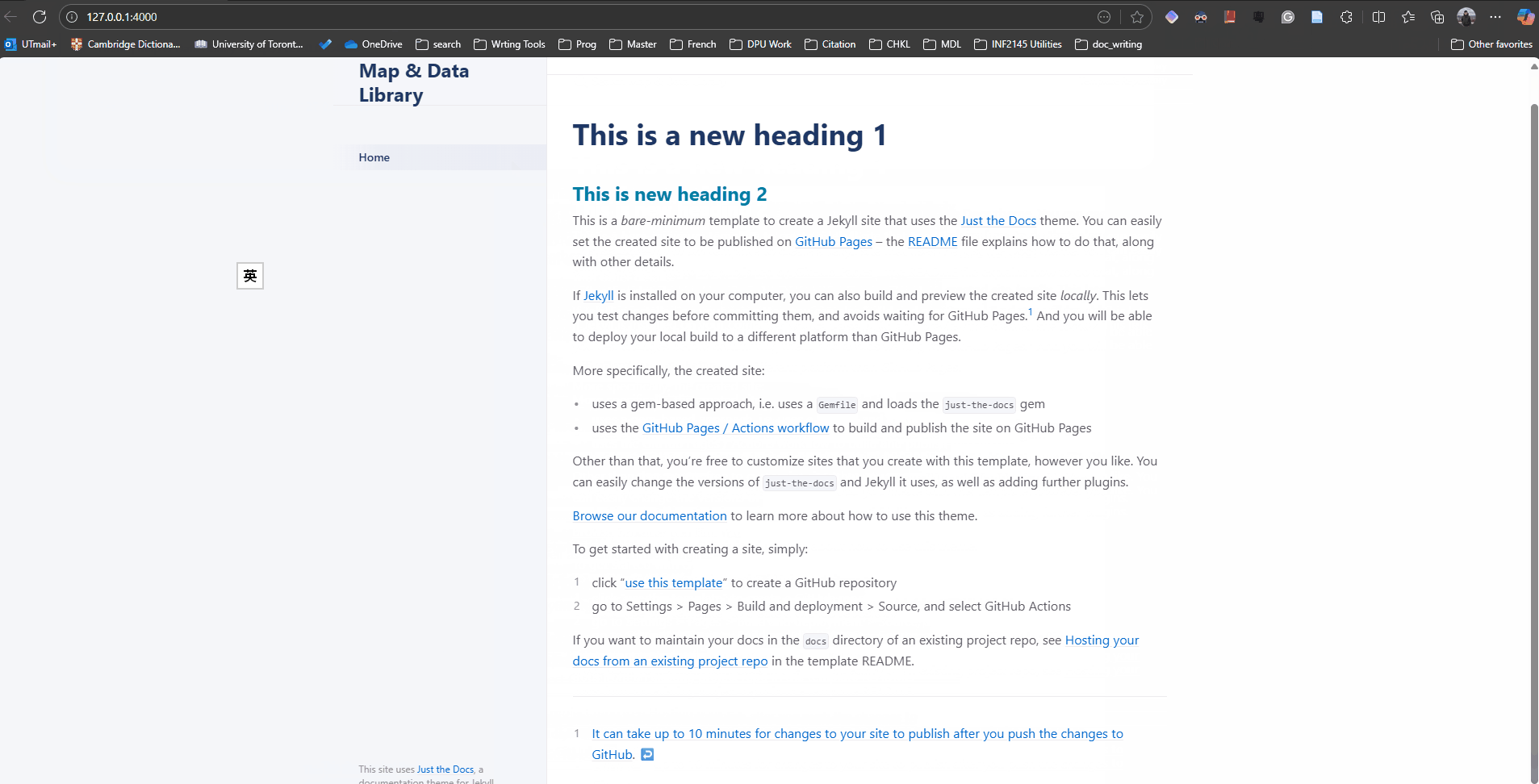
bundle installRun the following command to start the Jekyll server with live reload enabled
bundle exec jekyll serve --livereloadOnce you see the following message in the terminal, you may access the preview pages in your preferred web browser via http://127.0.0.1:4000 (or whatever address the terminal shows after the Server address line)
... You can add fiddle to your Gemfile or gemspec to silence this warning. LiveReload address: http://127.0.0.1:35729 Server address: http://127.0.0.1:4000 Server running... press ctrl-c to stop.